

Forearm fractures more commonly occur in men than women, owing to a higher incidence in men of participation in contact sports, altercations, falls from height, and motor vehicle collisions Anatomy Late complications include the following:Īn isolated fracture to the ulna often called a “nightstick” fracture, most often occurs during an altercation. ComplicationsĮarly complications of radial head or neck fractures or dislocations include the following: The surgical approach depends on the fracture location. Generally the standard of care for radial shaft fractures is open reduction and internal fixation. After swelling subsides, a long arm cast can be added. In the case of nondisplaced radial shaft fractures, initial immobilization in a splint will likely be the preferred treatment option. Non-operative treatment of radial shaft fractures is rare and outcomes of nonsurgical treatment in the past have been poor. If the fractures are not clearly seen on X-rays, delayed X-rays, MRI or CT scan will confirm the diagnosis further. If there is the deformity of the radius, your physician will conduct immediate clinical diagnosis on the injury and will confirm the analysis with the result of the X-rays and will conduct a differential diagnosis that will include the scaphoid and the wrist because fractures of the radius are always accompanied by wrist fractures. Diagnosisĭiagnosis of a radial shaft fracture comes from a history, physical examination and lateral radiographs of the elbow, forearm and wrist. It is located on the lateral side of the forearm parallel to the ulna (in anatomical position with arms hanging at the sides of the body, palms facing forward) between the thumb and the elbow. The radius is the thicker and shorter of the two long bones in the forearm. When an isolated radial shaft fracture occurs, it commonly requires surgery unless the fracture is non-displaced. More commonly, fractures of the radial shaft are associated with injury to the ulna. Radial Shaft FracturesĪn isolated fracture of the radial shaft is an unusual injury.
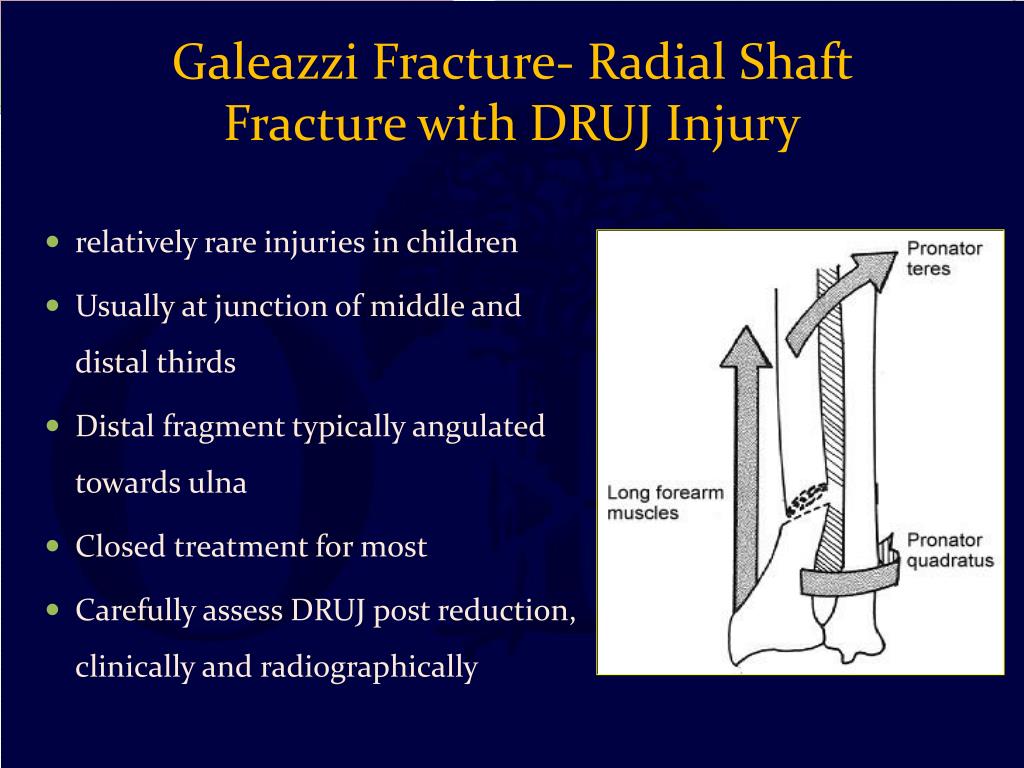
A broken forearm can affect your ability to rotate your arm and even bend or straighten the wrist and elbow. The forearm motion allows us to rotate our palms up or down. A fracture in the forearm can occur near the wrist, in the middle of the forearm or near the elbow. The forearm consists of two relatively parallel bones that connect two joints: elbow and wrist. However, proper reduction of the radius with concomitant reduction of the distal radioulnar joint and cast immobilization provides good to excellent outcome even if the Galeazzi lesion is primarily not recognized.The forearm is made up of two bones in your lower arm, the radius and ulna. In cases of distal forearm fractures, a possible Galeazzi lesion should be considered. The results were excellent in 23 cases and good in three cases. Thirteen patients were treated with immobilization in a below-elbow cast and nine with an above-elbow cast. Casting after fracture reduction was possible in 22 patients. Eight of 26 (31%) fractures were recognized initially and classified as a Galeazzi lesion. Outcome was assessed using the Gartland-Werley score. In 26 (13%) cases, a Galeazzi lesion was found and these patients formed the study group. One hundred ninety-eight patients with displaced fractures of the radius alone or both bones of the forearm were reviewed. The objective of this retrospectively designed study was to describe all Galeazzi lesions treated at our department during a 3-year period. Treatment in children and adolescents is usually possible with closed reduction and casting. A Galeazzi fracture is defined as a fracture of the radius associated with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
